
Sunorhc is a lightweight library for handling dates and times for JavaScript. The library wraps a native JavaScript Date object to create its own immutable date and time instance. The instance contains property values of date and time elements and various getters that can be used immediately. In addition, a rich set of instance methods are provided to easily perform date-time calculations and comparisons against a primitive base date-time.
Concept
Sunorhc is being developed to handle date and time as a core library for “Sunorhc.Timeline” (under development as of August 2021), the successor to “jQuery.Timeline“. The main objective is to be able to map the first year of the A.D. (January 1, 2012, 0:00:0:0) of the time axis as the original period so that the date and time can be easily handled as a single coordinate on the timeline. In addition, instance methods for adding and subtracting dates and getting periods are implemented “with the shortest possible method names”. It is also worth mentioning that it has like `date_format()` formatter in PHP.Also the setter is intentionally left out of the implementation, since overwriting the primitive value makes it difficult to understand the immutability of the instance itself.In developing Sunorhc, we took inspiration from various JavaScript date/time libraries such as “Luxon“, “DAYJS“, and “Temporal“, and enthusiastically incorporated specifications and features that we judged to be superior in each library.In addition, Sunorhc has been short-coded to be able to withstand use as a general-purpose date/time library, emphasizing a balance between generalization of implementation functions and readability. As a result, the final build file size after Minify is 26.2kB (as of version 1.0.2), and the Gzip compressed distribution size is further minimized to 6.96kB.Sunorhc will be able to be adopted as a front-end date-time library by itself (if you understand and can tolerate that features).
What is CE Epoch Time?
This is the most important feature of Sunorhc.
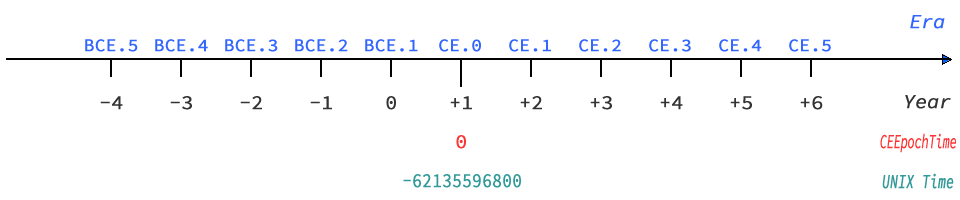
In addition to the UNIX time, which represents the elapsed time from the conventional UNIX epoch time (1970-01-01T00:00:00), Sunorhc instances also have an elapsed time from an epoch time is 0001-01-01T00:00:00 which the first year of the Common Era. Both UNIX time and CE epoch time can be obtained in milliseconds and seconds.
Note that UNIX time and CE epoch time do not support leap seconds.
There is also an option to create a date/time instance from CE epoch time or UNIX time.
Handling of year and month
Sunorhc instantiates the year as it is given, regardless of whether it is before or after C.E. There is no automatic mapping of two-digit years from 0 to 99 to 1900 or later, as there is with Date objects. It is easy to handle the year B.C. with negative years, but keep in mind that the year 1 BCE. will be 0.
Also, the months January through December in Sunorhc are directly interpreted as values 1 through 12. This is true for both input and output, although it is important to note that the index values for months in the Date object are 0-11, making it more intuitive to handle dates.
Dealing with Time Zones
In principle, the time zone of the date and time handled by Sunorhc instances is “UTC”. Sunorhc supports only “UTC” and other “local” time zones.
Sunorhc internally manages only the time zone offset, retrieving the time zone offset value on the system and generating the instance date and time according to that value. You can also specify a time zone name other than “local” that conforms to the Time Zone Database managed by IANA, but Sunorhc internally handles all time zone offset values other than 0 as “local”.
Observing of DST
When dealing with local time in Sunorhc instances, Daylight Saving Time (DST), which depends on some time zones, is supported. local time instantiated in Sunorhc includes the DST time difference, and the internally managed The time zone offset managed internally is also affected by the DST time difference. The details of whether the instance’s date and time are in DST and the time difference if they are in DST can be obtained via immediate properties, getters, and instance methods.
Note that DST will not be generated for dates and times instantiated with a time zone of “UTC”.
An Instance Construction
The specification of the instance created by the constructor of Sunorhc is as shown in the example below.
As an environment example, let’s assume that the system time zone is Asia/Tokyo (Japan Standard Time: UTC+09:00) and the current local time zone date and time (Japan Standard Time) is 2021-08-25 21:13:00.771.
| Constructor arguments | Example arguments (*1) | Instance datetime (*2) | Instance TimeZone (*3) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | None | 2021-08-25T12:13:00.771Z | UTC | The UTC date and time calculated from the local datetime will be instantiated. |
| TimeZone argument available | 'local' | 2021-08-25T21:13:00.771+09:00 | local (UTC+09:00) | Local datetime is instantiated. |
| TimeZone argument available | 'America/New_York' | 2021-08-25T21:13:00.771+09:00 | local (UTC+09:00) | Local datetime is instantiated (system TimeZone is applied instead of the specified TimeZone name). |
| Date and time payloads only | 2021, 6, 1 | 2021-06-01T00:00:00.000Z | UTC | UTC datetime of the specified by payloads will be instantiated. |
| Year only | 0 | 0000-01-01T00:00:00.000Z | UTC | UTC datetime of BCE. 1 is instantiated. |
| UNIX time | 0, {firstArgument: 'timestamp'} | 1970-01-01T00:00:00.000Z | UTC | UTC datetime of UNIX timestamp is instantiated. |
| CE epoche time | 0, {firstArgument: 'ce'} | 0001-01-01T00:00:00.000Z | UTC | UTC datetime calculated from the CE epoch time is instantiated. |
| Date and time payloads with TimeZone argument | 2021, 6, 1, 'local' | 2021-06-01T00:00:00.000+09:00 | local (UTC+09:00) | Local datetime of the specified payloads will be instantiated. |
| Datetime string | '2021/4/5 11:22:33' | 2021-04-05T11:22:33.000Z | UTC | Datetime that parsed the specified datetime string will be instantiated. |
| Date object | new Date() | 2021-08-25T12:13:00.771Z | UTC | UTC datetime calculated from the primitive value (UNIX time) of the Date object will be instantiated. |
| Date object | new Date(), 'local' | 2021-08-25T21:13:00.771+09:00 | local (UTC+09:00) | Local datetime by adding the system TimeZone offset to the UNIX time of the Date object will be instantiated. |
- The “example argument” is payloads of “args…” given to
new Sunorhc(args...). - The “instance datetime” is the string that can be retrieved with the getter
toISOString. - Information about the “Instance TimeZone” can be retrieved with the getters
timezoneandtzOffset.
As this example shows, Sunorhc does not handle dates and times in the local time zone in instances unless a time zone argument (such as local) is given to the constructor.
Note that you can use the getter toDate to convert a Sunorhc instance to a Date object, or use the instance methods getUTC() and getZoned() to convert the date and time between UTC and local time zone.
About Primitive Value
The primitive value of Sunorhc will be an instance of the native JavaScript Date object created by the constructor. As an entity, it is equivalent to the primitive value of the Date object, a number representing the number of milliseconds elapsed since the UNIX epoch.
If you want to reference a primitive value directly from an instance, you can use new Sunorhc(). _baseDate, but this reference is not recommended in many cases. Because the value stored in the _baseDate property is an instance of a pure Date object before it is finalized as a Sunorhc instance, and thus it is not consistent with the values of immediate properties, getters, and instance methods.
Normally, the _baseDate property should be made a private property, but Sunorhc does not require such robustness as a library.
As for the actual instance of using Sunorhc, the instant property described next plays a role.
Instant Property
The instance created by Sunorhc holds an instant object called instant property. This object contains various element snippets of the instantiated date and time data. The elements included in the instant property are as follows.
| property(instant.*) | Getter | Data Type | Data Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| $Y | year | Integer | Integer representing the year in Arabic numerals (negative value prior to BCE.1) |
| $MON | month | Integer | Integer representing the month in Arabic numerals (1-12) |
| $MONL | monthLong | String | Capital case string representing the month in English notation (e.g. January) |
| $MONS | monthShort | String | First three characters of the capital case string representing the month in English notation (e.g. Jan) |
| $W | week | Integer | Integer representing the ordinal week number of the year in Arabic numerals |
| $D | day | Integer | Integer representing the date in Arabic numerals |
| $WD | weekday | Integer | Integer representing the number of the day of the week in Arabic numerals (1:Monday – 7:Sunday, according to ISO 8601) |
| $WDL | weekdayLong | String | Capital case string representing the day of the week in English notation (e.g. Monday) |
| $WDS | weekdayShort | String | First three characters of the capital case string representing the day of the week in English notation (e.g. Mon) |
| $O | ordinalDays | Integer | Integer representing the ordinal days number in the year in Arabic numerals (0-365) |
| $H | hour | Integer | Integer representing the hours in Arabic numerals (0-23) |
| $M | minute | Integer | Integer representing the minutes in Arabic numerals (0-59) |
| $S | second | Integer | Integer representing the seconds in Arabic numerals (0-59) |
| $MS | millisecond | Integer | Integer representing the milliseconds in Arabic numerals (0-999) |
| $TZ | timezone | String | String representing the TimeZone name (either UTC or local) |
| $TZO | tzOffset | Integer | Integer representing the TimeZone offset in Arabic numerals (in milliseconds) |
| $TZOL | tzOffsetHM | String | String representing the TimeZone offset (in ±HH:MM format with seconds and less truncated) |
| $TZOF | tzOffsetFull | String | String representing the TimeZone offset (in ±HH:MM:SS.mmm format) |
| $U | unix (*1) | Integer | Integer representing UNIX time in Arabic numerals (in seconds) |
| $UMS | unix (*1) | Integer | Integer representing UNIX time in Arabic numerals (in milliseconds) |
| $E | era | String | A string representing the era in English notation |
| $CE | ce (*1) | Integer | Integer representing the CE epoch time in Arabic numerals (in seconds) |
| $CEMS | ce (*1) | Integer | Integer representing the CE epoch time in Arabic numerals (in milliseconds) |
| $DST | — | Boolean | Boolean value indicating whether or not DST is observed in datetime |
| $DSTO | — | Integer | Integer representing the DST offset in Arabic numerals (in milliseconds) |
- The acquisition unit can be specified in the constructor argument
epochUnit. The initial value is seconds.
The instant property is an immutable value as well as the date and time data held internally. Basically, the various getters are like aliases for retrieving these instant properties with interactive descriptions.
Supported Browsers
The actual working environment and supported browsers of Sunorhc are as follows.
| Chrome (>= 92) | firefox (>= 91) | Safari (>=13) | Edge (>= 92) | Android | iOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓(*1) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
- Note: “Intl.Locale” object is not supported by native JavaScript in Safari 13, so a separate Polyfill is required for formatter language resolution.
Please note that we have not checked the operation of the software on legacy browsers such as IE. We do not plan to provide support for these legacy browsers.
Installations
NPM
npm install sunorhcIf you are using Yarn, it will be yarn add sunorhc.
GitHub
git clone https://github.com/ka215/sunorhc.gitThe built JS files are stored in the dist directory of the repository.
Usage
Sunorhc can be used by itself by loading the script file after it is built.
Node
const Sunorhc = require('sunorhc')
const NOW_UTC = new Sunorhc()ES6
import Sunorhc from 'sunorhc'
const NOW_ZONED = new Sunorhc('local')HTML5
<script src="/path/to/sunorhc.min.js"></script>
<script>
const NOW_UTC = new Sunorhc()
</script>It is also possible to load via CDN.
<script src="https://unpkg.com/sunorhc@latest/dist/sunorhc.min.js"></script>Examples of Use
Constructor
const NOW_UTC = new Sunorhc()
const DateTime = new Sunorhc(2021, 8, 23, 22, 57, 'local')
console.log(DataTime.toISOString) //=> 2021-08-23T22:57:00.000+09:00
const DT1 = new Sunorhc(123456789000, { firstArgument: "timestamp" }),
DT2 = new Sunorhc(123456789000, { firstArgument: "ceepoch" })
console.log(
DT1.toISOString, //=> 1973-11-29T21:33:09.000Z
DT2.toISOString, //=> 0004-11-29T21:33:09.000Z
)Getter
const NOW_UTC = new Sunorhc()
console.log(
NOW_UTC.toISOString, //=> 2021-08-23T14:11:34.249Z
NOW_UTC.monthLong, //=> August
NOW_UTC.weekdayLong, //=> Monday
NOW_UTC.hour, //=> 14
NOW_UTC.tzOffsetHM, //=> +00:00
NOW_UTC.era, //=> 8 23, 2021 Anno Domini
)Instance Methods
const DateTime = new Sunorhc()
console.log(
DateTime.format('Y-m-d H:i:s'), //=> 2021-08-23 15:21:02
DateTime.getLDE('weekday', 'long', 'en-US'), //=> Monday
DateTime.modify(+1, 'month').toISOString, //=> 2021-09-23T15:24:20.070Z
DateTime.modify(-1, 'day').toString, //=> Sun Aug 22 2021 15:24:20 GMT+0000 (UTC)
DateTime.interval('2021-10-20', 'day'), //=> 58
DateTime.getISO('ordinal'), //=> 2021-234
)Documentations
Sorry, currently writing the manual document.
Repository
https://github.com/ka215/sunorhc
https://www.npmjs.com/package/sunorhc
Lisence
Code released under the MIT License.
